Table of Contents
The Cost of Hearing Aids and Insurance Coverage

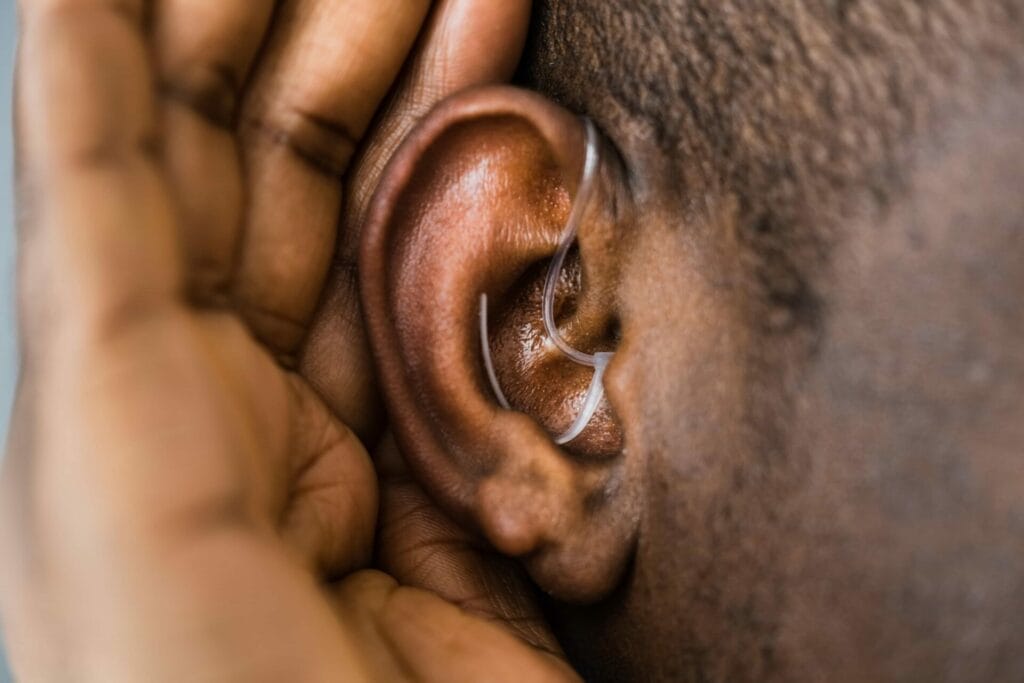
Hearing is one of our most essential senses, playing a pivotal role in how we communicate, connect with others, and perceive the world around us. For those with hearing impairments, the challenges can be immense, affecting not just their personal interactions, but also their overall quality of life. In such scenarios, hearing aids emerge as a beacon of hope, offering the promise of clearer communication and an enhanced auditory experience.
However, while the technological advancements in hearing aids have been remarkable, making them more effective and user-friendly, they also come with a significant price tag.
For many Australians, the cost of these devices can be a major deterrent, especially when considering that hearing aids are not a one-time purchase but require ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and replacements.
The financial burden of hearing aids is further compounded when individuals realise that not all insurance policies or health schemes cover these devices comprehensively. As a result, many are left navigating a maze of costs, coverage gaps, and financial decisions, trying to find a balance between affordability and the quality of hearing care.
The True Cost of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids, while essential for many individuals with hearing impairments, can pose a significant financial challenge. Understanding the breakdown of costs can help prospective buyers make informed decisions.
- Purchase Price of the Device Itself. The bulk of the expense often lies in the device’s purchase price. Depending on the brand, model, and features, hearing aids in Australia can range from AUD 800 for basic models to over AUD 4,000 for premium devices.
- Fitting and Consultation Fees. Before purchasing a hearing aid, patients usually undergo a series of tests and consultations with an audiologist. These tests determine the type and degree of hearing loss and help in selecting the right device. Consultation fees can range from AUD 50 to AUD 500 or more, depending on the clinic and the complexity of the patient’s needs.
- Maintenance and Repair Costs. Like any electronic device, hearing aids require regular maintenance to function optimally. This includes periodic cleaning, software updates, and minor repairs. While some of these costs are minimal, significant repairs outside the warranty period can run into hundreds of dollars.
- Replacement Parts and Batteries. Over time, parts like ear domes, tubes, or wax filters will need replacement. Additionally, unless one opts for rechargeable hearing aids, batteries will be a recurring expense. While individual batteries are relatively cheap, costing a few dollars for a pack, their cumulative cost over the years can be substantial.
- Technology Upgrades and Features. Modern hearing aids come packed with features like Bluetooth connectivity, noise cancellation, and tinnitus masking. While these features can significantly improve the user experience, they also contribute to the device’s overall cost. It’s essential to weigh the benefits of these features against their costs.
While the sticker price of a hearing aid provides an initial cost estimation, it’s the aggregate of these various expenses that gives a truer picture of the financial commitment involved. Prospective buyers should factor in all these costs when budgeting for a new hearing aid to avoid any unwelcome surprises.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Hearing Aids in Australia
The cost of hearing aids can vary widely, and several factors play into how much one might spend on these essential devices. Understanding these factors can help consumers make informed decisions and potentially save money.
Different Brands and Their Price Ranges
Just like any other product, hearing aids come in a range of brands, each with its reputation, features, and price points. Established brands such as Oticon, Bernafon, Signia, Phonak, and ReSound might carry a premium due to their long-standing presence in the market and the trust they’ve built over the years. However, newer brands or less-known manufacturers might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
Technological Advancements and Premium Features
Modern hearing aids are not just about amplifying sound; they come with a host of features that can significantly impact their cost:
- Bluetooth connectivity: Allows users to connect their hearing aids directly to smartphones, TVs, or other devices.
- Noise-cancellation: Helps users focus on conversations by reducing background noises.
- Rechargeable batteries: Offers the convenience of not having to replace batteries regularly.
While these features enhance user experience, they can also add to the overall cost of the device.
Customisation Options
- Style and Type: The cost can vary depending on the style of the hearing aid. For instance, completely-in-canal (CIC) models might be priced differently than behind-the-ear (BTE) models.
- Color Choices: Some brands offer a range of colors and finishes, allowing users to choose a device that matches their aesthetic preferences or is more discreet.
- Special Molds: Custom-molded hearing aids, tailored to the user’s ear, can be pricier than standard models.
Professional Services
- Audiologist Consultations: An essential part of the hearing aid journey is consulting with an audiologist. They assess hearing levels, recommend appropriate devices, and often play a role in fitting and fine-tuning the aids. Their expertise comes at a cost, which can vary based on their experience and location.
- Fittings: Properly fitting a hearing aid can take multiple visits and adjustments, adding to the overall expense.
- Aftercare Services: Regular check-ups, cleanings, and recalibrations are crucial for the longevity and efficiency of hearing aids. Some providers might offer these services as part of a package, while others might charge separately.
While the base price of a hearing aid provides an initial understanding of its cost, it’s essential to factor in these additional considerations. It ensures that users are not caught off-guard by unexpected expenses and can budget appropriately for their hearing health.
The Australian Insurance Landscape
Australia boasts one of the world’s most comprehensive health care systems, which is supported both by government schemes and private health insurance. When it comes to the specific realm of hearing aids, the interplay between these two entities becomes crucial for individuals seeking financial relief.
Private Health Insurance and Hearing Aids
Most Australians are familiar with the two tiers of private health insurance: hospital and extras. While hospital policies cover in-patient treatments, it’s the extras policies that pertain to out-of-hospital services like dental, optical, and, in many cases, hearing aids. Here’s what to consider:
- Coverage Variability: Not all extras policies cover the cost of hearing aids. Those that do might offer varying amounts of coverage, ranging from partial to full, depending on the level of the policy.
- Claim Limits: Even if hearing aids are covered, there’s often a limit to the claimable amount, either annually or over a set number of years. This is crucial to check, as hearing aids can be a significant investment.
- Waiting Periods: Many policies impose waiting periods for certain services, meaning you’d need to hold the policy for a specified duration (often 12 months or more) before making a claim for hearing aids.
- Workers’ Compensation: For individuals whose hearing loss is attributed to their work environment—be it sudden trauma or prolonged exposure to noise—there’s the possibility of claiming hearing aids through workers’ compensation. Each state and territory in Australia has its own workers’ compensation scheme, and the specifics can vary:
- Eligibility: To be eligible, one must demonstrate that the hearing loss is work-related. This typically requires an audiometric assessment and potentially other documentation.
- Coverage Extent: If deemed eligible, the extent of coverage can vary. Some schemes might cover the full cost of hearing aids, while others might contribute a fixed amount.
- Other Specialised Insurance Policies: Beyond the traditional avenues, there are specialized insurance policies tailored for specific needs. Some older Australians might have acquired hearing aids coverage as part of life insurance or retirement plans, while others might find niche policies catering specifically to hearing health.
Navigating the Australian insurance landscape in the context of hearing aids can seem daunting. However, by understanding the intricacies of different policies and being proactive in checking coverage details, individuals can significantly mitigate the financial burden of acquiring these essential devices.
The Extent of Coverage
Hearing aids, due to their necessity for many, often find a place in health insurance policies, but the depth and breadth of coverage can vary significantly between providers and policy types. Understanding this coverage can be the difference between a manageable expense and a prohibitive cost. Here’s what you need to know:
Typical Coverage Amounts and Limits. Most private health insurance policies that cover hearing aids in Australia tend to set a capped benefit amount. This means there’s a maximum amount the insurer will pay towards the cost of the hearing aids. For instance, a policy might offer $1,000 every three years for hearing aids. This doesn’t mean the hearing aids will only cost $1,000; it means the insurance will contribute that amount, and any additional costs will be out-of-pocket for the policyholder.
Out-of-Pocket Costs for Patients. Even with insurance coverage, many Australians find themselves paying some amount out-of-pocket. The gap between the insurance benefit and the actual cost of the hearing aid can vary, but it’s not uncommon for individuals to pay several hundred to over a thousand dollars, especially if they opt for higher-end models or additional features. It’s also essential to factor in other costs, such as consultations, fittings, and potential maintenance, which might not be fully covered by insurance.
Potential Waiting Periods Before Claiming. Most health insurance policies have waiting periods for certain services, and hearing aids are no exception. A waiting period is the time you need to wait after buying the policy before you can claim a benefit. For hearing aids, this can often be anywhere from 6 months to several years, depending on the policy. It’s crucial to be aware of these waiting periods, especially if you anticipate needing hearing aids soon.
Variability Between Providers. Just as every individual’s hearing needs are unique, so too are the policies offered by different insurance providers. Some may offer more generous benefits, shorter waiting periods, or coverage for a broader range of hearing-related services. It’s always a good idea to shop around, compare policies, and read the fine print. If in doubt, contact the insurance provider directly and ask specific questions about hearing aid coverage.
Government Assistance
Hearing loss affects a significant portion of the Australian population, both young and old. Recognizing the importance of providing support to those with hearing impairments, the Australian Government has instituted measures to make hearing services more accessible and affordable.
Australian Government’s Hearing Services Program
The centrepiece of this assistance is the Hearing Services Program (HSP). This program aims to provide eligible people with access to high-quality hearing services and devices. Administered by the Department of Health, the HSP offers a range of services, including:
- Comprehensive hearing assessments.
- Provision of hearing aids.
- Rehabilitation programs for individuals with hearing loss.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for the HSP, individuals typically need to meet certain criteria. These often include:
Being an Australian citizen or permanent resident aged 26 years or older.
Being a Veteran Affairs cardholder.
Receiving specific Centrelink payments, such as the Age Pension or Disability Support Pension.
Being a member of the Australian Defence Force.
Note: Eligibility criteria may change over time, so it’s crucial to consult the official HSP website or contact a hearing services provider for the most up-to-date information.
How to Apply
Applying for the HSP is a straightforward process:
- Check Eligibility: As mentioned above, ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria.
- Choose a Provider: You can select from a range of approved service providers. A list is available on the HSP website.
- Complete the Application: Fill in the necessary application forms, which are available online or from your chosen provider.
- Submit the Application: Once completed, submit the form either online or via post, as directed.
What’s Covered Under the Program
Under the HSP, eligible individuals can access:
- A comprehensive hearing test.
- A recommendation for suitable hearing devices if required.
- The fitting and adjustment of hearing devices.
- Training on how to use and care for the hearing aids.
- Ongoing maintenance and support for the devices.
In some cases, the program may cover the full cost of basic hearing aids. However, individuals can choose to pay the difference for more advanced or specialized devices if they wish.
Tips for Making Hearing Aids More Affordable
Hearing aids can be a significant investment, but their importance for quality of life and communication cannot be overstated. For those who find the cost prohibitive, there are several strategies to consider that can make these essential devices more affordable:
1. Shop Around:
Comparative Shopping: Just as you would with any major purchase, shop around. Different audiologists and hearing aid retailers might offer different prices or package deals.
Seek Promotions: Some stores may have periodic promotions, discounts, or sales events. It’s worth keeping an eye out and asking about any upcoming deals.
2. Negotiate:
Be Open: Don’t hesitate to discuss your budget constraints with your audiologist or the sales representative. They might offer flexible payment plans or direct you to less expensive models that still meet your needs.
Package Deals: Some providers may offer discounts if you purchase additional services or products, like extended warranties or bulk batteries.
3. Consider Older or Refurbished Models:
Previous Generations: While the latest technology might be tempting, previous generation models can be just as effective and come at a fraction of the cost.
Certified Refurbished: Some providers offer certified refurbished hearing aids that have been thoroughly tested and come with a warranty, offering significant savings.
4. Payment Plans and Financing:
Interest-Free Periods: Some providers offer interest-free payment plans, allowing you to spread out the cost over several months or even years.
Healthcare Credit Cards: Specialized credit cards for healthcare expenses sometimes offer promotional financing options, like no interest if paid in full within a certain timeframe.
5. Seek Donations or Grants:
Non-Profit Organisations: Some charitable organizations provide hearing aids to those in need. It’s worth researching local and national organisations that might offer such programs.
Community Grants: Occasionally, community groups or local businesses may offer grants or sponsorships for healthcare needs, including hearing aids.
While the initial sticker price of hearing aids can be daunting, exploring these avenues can lead to considerable savings. Remember, the goal is to find a solution that meets your hearing needs without compromising your financial well-being.
The Future of Hearing Aid Costs and Coverage
As with most technology, the world of hearing aids is constantly evolving. The industry’s future, both in terms of technological advancement and financial accessibility, is promising. Here’s what we can anticipate in the coming years:
Technological Innovations
Miniaturisation: As technology becomes more advanced, hearing aids are expected to become even smaller and more discreet, offering wearers enhanced comfort without compromising on functionality.
Integration with Smart Devices: The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) will likely see hearing aids integrated with other smart devices. Imagine your hearing aid adjusting its settings based on the ambient noise levels detected by your smartphone or even syncing with your smart home system to alert you when someone’s at the door.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven hearing aids could automatically adapt to different listening environments, making it easier for wearers to converse in noisy settings or focus on a specific sound source.
Pricing Trends
Economies of Scale: As more people become aware of hearing health and seek out aids, manufacturers might benefit from economies of scale, leading to reduced production costs and potentially lower retail prices.
Over-the-counter Hearing Aids: There’s a global trend toward legalising over-the-counter hearing aids, which can be sold without the need for a prescription. If this trend reaches Australia, it could introduce competitive pricing and make basic hearing aids more accessible.
Insurance and Government Initiatives
Expanded Coverage: With the increasing recognition of hearing health as a vital aspect of overall well-being, Australian insurance providers might expand their coverage options or offer more competitive premiums for hearing-related services.
Government Programs: The Australian government’s continued commitment to hearing health might result in expanded eligibility criteria or increased funding for the Hearing Services Program, ensuring that more Australians can access quality hearing care.
Advocacy and Awareness
Public Awareness Campaigns: As awareness about hearing health grows, there might be more public and private sector initiatives aimed at educating Australians about the importance of regular check-ups and early intervention.
Consumer Advocacy: Stronger advocacy movements can influence both manufacturers and policymakers. As consumers demand more affordable and high-quality devices, the industry might respond with innovations that meet these needs without inflating costs.
Conclusion
Hearing aids, for many, are not just a luxury but a necessity, enabling clearer communication, better quality of life, and improved mental well-being. In Australia, as in many parts of the world, the financial barrier to acquiring these devices is significant. This emphasizes the importance of being well-informed about the various costs associated with hearing aids and the avenues available to offset or manage these expenses.
While the initial investment in hearing aids might seem daunting, understanding the broader landscape of insurance coverage, government support, and other available resources can make this essential health tool more accessible. It’s crucial to remember that the cost of hearing aids isn’t just about the device itself but encompasses the holistic experience: the consultations, fittings, maintenance, and potential upgrades.
Additionally, as consumers and advocates, it’s beneficial to stay updated on the evolving market trends, insurance policies, and government initiatives. Changes in these areas can offer new opportunities for affordability and accessibility. Being proactive, researching, and asking the right questions can lead to significant savings and ensure that those in need receive the best care possible.
Lastly, as we navigate the intricate financial web surrounding hearing aids, it’s essential to remember the invaluable benefits they bring. The ability to connect with loved ones, participate in social activities, and simply enjoy the sounds of the world around us is truly priceless. The pursuit of better hearing and improved quality of life is an investment worth making, and with the right knowledge and resources, it becomes a more achievable goal for all Australians.
Additional Resources
To further assist you in navigating the financial complexities of hearing aids in Australia, here are some relevant organisations, programs, and sources:
Organisations and Programs
Hearing Services Program
Overview: A leading hearing specialist and largest provider of government-funded hearing services.
Website: Australian Hearing Services
Hearing Care Industry Association (HCIA)
Overview: Represents manufacturers and distributors of hearing devices in Australia.
Website: HCI
Deafness Forum of Australia
Overview: Represents all Australians who are deaf or have a hearing impairment or a chronic ear disorder.
Website: Deafness Forum of Australi
National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS)
Overview: Provides support for Australians with disability, including those with significant hearing loss.
Website: NDIS
By tapping into these resources, individuals can empower themselves with the knowledge and support needed to make informed financial decisions regarding hearing aids in Australia.
Sign Language
Another option for communication is to use sign language. This is a language that uses hand gestures, body language, and facial expressions to communicate. It is a visual language, so it does not require the use of sound. This can be a good option for people who are deaf or have severe hearing loss.
- Auditory-Oral. Auditory-oral communication is a method of communication that uses both hearing and speech. This can be a good option for people who have some hearing loss. It involves using lip reading, sign language, and other strategies to communicate.
- Aural Rehabilitation. Aural rehabilitation is another option for people with hearing loss. It is a program that helps people learn how to manage their hearing loss. It can help people learn how to use hearing aids, listen to the speech, and communicate better.
- Bilingualism. Bilingualism is another option for communication. It is a way of using two languages to communicate. This can be a good option for people who have hearing loss and speak two languages.
- Cued Speech. Cued speech is a system of communication that uses hand gestures to help people understand the sounds of speech. It can be a good option for people who have hearing loss.
- Total Communication. Total communication is a way of using all forms of communication to communicate. This can be a good option for people who have hearing loss.
Conclusion:
There are many ways to manage hearing loss. Some people use hearing aids, while others use sign language or lip reading to help them communicate. It is important to find the best way to manage the hearing loss that works for you. Talk to your doctor or a hearing specialist to find out more about the options available to you.
Using all methods of communication is ideal for those with hearing loss. Different individuals will have different levels of success with various modes of communication, so it is important to try out several before settling on the best method for you. Ask for help from a doctor or hearing specialist to find the best way to manage your hearing loss.

DISCLAIMER:
The information on this website is provided for educational purposes only. We do not support, nor recommend any products or treatments without proper hearing diagnostic and proper hearing evaluation. All users must seek professional advice before beginning treatment as well as inform themselves of known side effects/risks associated with said procedure(s).
Check more related topics below.
Of our 5 senses, hearing is probably the most important for our feeling of connection to the world around us. It allows us to communicate with friends and family, enjoy the sounds around us like music or nature and helps keep us safe by alerting us to warning signals, the various sounds in traffic and other forms of danger. To properly understand how we conduct a hearing test, it is best to understand how the ear works.
